- 名前:
- 正岡 真一
- 学年/肩書:
- 卒業生
- 役職:
- したっぱの総長
- グループ:
- ロボット
- 趣味:
- 楽器演奏
- 一言:
- 歳の数だけ論文執筆
研究テーマ / Research topic
身体との『接触状態』を制御可能な装着型アシストロボットの開発
論文が採択されました。
※出版に伴って予告なく削除されることがあります。
【論文PDF】Gravity Compensation Method for Whole Body-Mounted Robot with Contact Force Distribution Sensor
| English ver. | 日本語版 |
ap
ROBOT USED IN MY RESEARCH
Here is the robot we are using in our current experiment.

Full Body-Mounted Robot
Although the robot cannot walk yet, it is able to measure the contact force acting between the robot and the human body without omission in full body movements, such as bending down and lifting objects.
![]()
We measured what kind of force is being exerted on which parts of the body while wearing this robot and performing bending and extending exercises.
| Left-Side of Movie | Right-Side of Movie | ||
| Upper Front | Upper back | ||
| Middle Front | Middle Back | ||
| Under Front | Under Back | ||
| Left Calf Front | Right Calf Front | Left Calf Back | Right Calf Back |
| Left Shin | Right Shin | Left Thigh | Right Thigh |
Using this data as a reference, what parts of the robot should be changed to make it even more comfortable to wear? Or how can we control the robot to reduce the force concentrated somewhere as our research?
BACKGROUND
Ensuring the safety of the wearer is an important issue for wearable robots used for motion support applications. Existing wearable robots are generally controlled by measuring the load applied to the wearer’s joints using torque sensors in the robot’s joints. However, this method does not directly measure the force applied to the body surface of the robot wearer. Thus, it means that even if a dangerous force is exerted or pressure is felt, it is not seen for forces that do not involve the sensors at the joints.
My goal is to realize safe motion support with a robot that can measure and control contact force distribution information by installing pressure distribution sensors in the contact area between the wearer and the robot.
About the robot configuration
.
I will introduce the configuration of how the wearer’s contact force is actually measured, using the arm as an example.
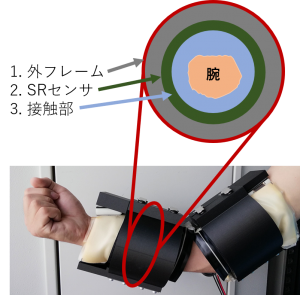
Robots Fabricated in Prior Research
1. Outer Layer The most outwardly rigid cylindrical shape is used. This is to assist the arm without deformation and to minimize disturbance to the pressure distribution sensor (constant and smooth curvature of the surface).
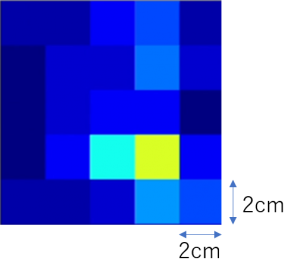
Image of Pressure Distribution Sensor: Brighter Color Means Greater Contact Force)
2. Sensor Layer Pressure distribution sensors (SR sensor) are 2 cm square cells that are affixed to every part of the robot that comes in contact with the body.

Personal Body Surface Shape Data Used for The Contact Area
3. Contact Layer The Contact Layer is constructed using an individual’s body surface shape measured with a 3D camera, using an average body surface shape so that anyone can fit, or simply filling in the gaps with sponges, depending on the body part.
ap
研究で使っているロボット
こちらが今の実験で使っているロボットです。

全身装着型ロボット
このロボットは、まだ歩くことはできませんが、かがんでモノを持ち上げる、といった全身の動作において、ロボットとの接触状態を漏れなく取得することができます。
![]()
実際に、このロボットを装着して屈伸運動をしながら、どの部位にどんな力が働いているのか、を計測しています。
| 動画左側 | 動画右側 | ||
| 胸 | 背中 | ||
| 腹 | 腰 | ||
| 腹下 | 腰下 | ||
| 左ふくらはぎ表 | 右ふくらはぎ表 | 左ふくらはぎ裏 | 右ふくらはぎ裏 |
| 左脛 | 右脛 | 左太もも | 右太もも |
このデータを参考にしながら、どの部分をどう変更したらさらに付け心地の良いロボットになるのか。あるいはどのようにロボットを制御すればどこかに集中した力を減らすことができるのか、を研究として考えています。
研究背景
動作支援用途の装着型ロボットにおいて、装着者の安全性確保は重要課題です。既存の装着型ロボットでは、ロボット関節部のトルクセンサにより人の関節部に加わる負荷を計測し、ロボットを制御することが一般的でした。しかしこの手法は、ロボット装着者の体表面に加える力を直接計測しているわけではありません。したがって、危険な力が働いたり、圧迫感があったとしても、関節のセンサに関与しない力については見られないということです。
私は、装着者とロボットの接触部に圧力分布センサを搭載し、接触力分布情報を計測・制御可能なロボットによる安全な動作支援の実現を目指しています。
ロボットの構成について
実際にどのようにして装着者の接触力を計測するのか、腕部を例にして構成を紹介します。

先行研究で制作されたロボット
1. 外フレームとして、もっとも外側には硬い円筒形状のものが用いられています。変形せずに腕をアシストすることと、圧力分布センサへの外乱が少ない(面の曲率が一定かつなめらか)ことを考慮しています。

圧力分布センサのイメージ(色が明るいほど接触力が大きい)
2. SRセンサとは、圧力分布センサのことです。2cm四方のセルが、ロボットの各部位で体に接触するヵ所にもれなく貼付しています。

接触部に使った個人の体表面形状データ
3. 接触部は3Dカメラを使って計測した個人の体表面形状を用いたり、誰でもフィットできるように平均的な体の体表面形状を用いたり、あるいは体の部位によっては単にスポンジで隙間を埋めるなどで、構成されています。