研究テーマ / Research topic
拡張誘起電圧を利用した永久磁石同期モータの位置センサレス制御における始動時間の短縮
| English ver. | Japanese ver. |
私は、拡張誘起電圧を利用した永久磁石同期モータの位置センサレス制御について研究を行っています。現在は、位置センサレス制御の始動時間を短縮可能な手法にの検討に取り組んでいます。
ap
永久磁石同期モータ(PMSM)とは?
永久磁石同期モータ(PMSM: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor)は、三相交流電圧によって駆動される交流モータで、小形で高出力密度、かつ高効率といった特徴を持っています。そのため、エアコンのコンプレッサ等の家電分野や、マニピュレータ等の産業分野、電気自動車等の移動体分野など実に幅広い分野で利用されています。
位置センサとは?
PMSMを制御するためには、回転子の内部にある磁石のN極の向き(磁極位置情報)に合わせて適切に三相電圧を印加する必要があります。通常は、磁極位置情報を取得するためにはモータ軸上に位置センサを取り付ける必要があります。しかし、位置センサを利用すると、コストの増加や、設置スペース、配線の断線リスク等の問題点が生じてしまいます。その結果、モータを搭載した家電や電気自動車に対しても、価格の上昇やサイズの増加に繋がります。また、アプリケーションによっては、そもそもモータに位置センサが取り付けられないこともあります。
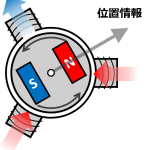
図1. PMSM概略図
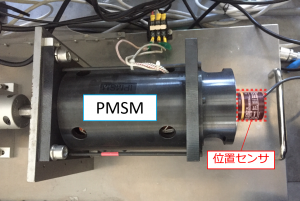
図2. PMSMと位置センサ
位置センサレス制御とは?
位置センサ設置の問題点を解決策として、位置センサレス制御が提案されています。位置センサレス制御では、位置センサの代わりに、印加電圧・測定電流と数式モデルから位置情報を計算することで位置センサが不要になります。この計算はソフトウェア(=制御プログラム)の書き換えのみで実現可能であるため、ハードウェアの変更は不要です。

図3. 位置センサ付き制御

図4. 位置センサレス制御
現在の取り組み
位置センサレス制御における課題の一つに、始動時間が挙げられます。位置センサレス制御では、位置推定の開始時には位置の初期値が不明であるため、初期値の推定が完了するまでの時間(=始動時間)が必要になります。モータの回転指令と同時に位置推定を開始した場合、始動時間の分だけ出力までのタイムラグが生じてしまいます。
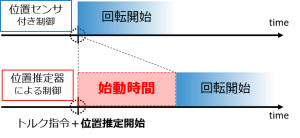
図5. 位置センサレス制御の始動時間
そこで、私はこの始動時間の短縮について研究しています。数式モデルは、始動から高速まで、全速度域の推定に適しているという理由から、拡張誘起電圧(EEMF)モデルを使用しています。
これまで、始動に用いる信号の見直しにより始動時間を従来の3分の1程度に短縮可能な手法の提案を行いました。現在の取り組みとしては、様々なモータでの実験結果から調整項目やアルゴリズムの見直しを行い、より最適な手法への改良を試みています。
EEMFに関する関連研究
・二村 拓未, 道木 慎二: “信号重畳と速度により励起される拡張誘起電圧を利用した永久磁石同期モータの全速度域位置センサレス制御”, 電学論D, vol.140, No.8, pp.589-596
・近藤 翔太, 道木 慎二, 松本 純, 冨田 睦雄: “PMSM位置センサレス制御のための仮想誘起電圧に基づく制御用モデルに関する考察”, 電学論D, vol.139, No.1, pp.1-12
English.ver
I study the position sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors using Extended-Electromotive Force(EEMF). I am currently working on a method to reduce the starting time of the position sensorless control.
ap
What is Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors?
PMSMs are AC motors driven by three-phase AC voltage, and are characterized by their small size, high power density, and high efficiency. For this reason, they are used in a wide range of fields, including home appliances such as air conditioner compressors, industrial fields such as manipulators, and mobile fields such as electric vehicles.
What is Position Sensor?
In order to control a PMSM, it is necessary to properly apply three-phase voltage according to the direction of the N-pole of the magnet inside the rotor (magnetic pole position information). Normally, it is necessary to install a position sensor on the motor shaft in order to obtain the magnetic pole position information. However, the use of a position sensor causes problems such as increased cost, installation space, and risk of wiring breakage. As a result, it will also lead to higher prices and increased size for home appliances and electric vehicles equipped with motors. Also, depending on the application, it may not be possible to install a position sensor on the motor in the first place.
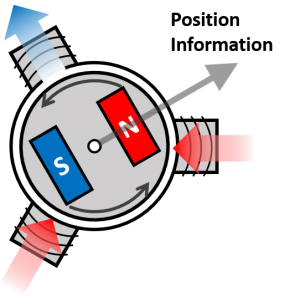
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of PMSM
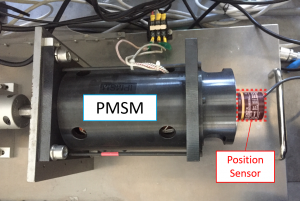
Fig.2 PMSM and position sensor
What is Position Sensorless Control?
Position sensor-less control has been proposed as a solution to the problem of position sensor installation. In position sensor-less control, the position information is calculated from the applied voltage and measured current and the mathematical model. Therefore, a position sensor is no longer required. This calculation can be achieved only by rewriting the software, i.e., the control program, so no hardware changes are required.
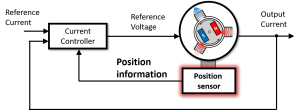
Fig.3 Control system with position sensor
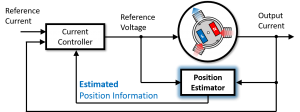
Fig.4 Position sensorless control system
Research Introduction
One of the challenges in position sensorless control is the startup time. In position sensor-less control, the initial value of the position is unknown at the start of position estimation, so time is required to complete the estimation of the initial value, i.e., start-up time. If the position estimation is started at the same time as the motor rotation command, there will be a time lag to the output due to the start-up time.
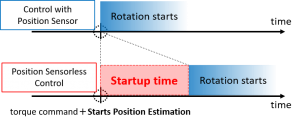
Fig.5 Startup time of position sensorless control
Therefore, I am studying the reduction of this starting time. As a mathematical model, I use Extended-Electromotive Force (EEMF) model because it is suitable for estimating the entire speed range from start to high speed.
I have proposed a method that can reduce the starting time to about one-third of the conventional method by reviewing the signals used for starting. My current efforts include reviewing the adjustment items and algorithms based on the results of experiments with various motors, and trying to improve the method to be more optimal.
Reference for EEMF
[1] T. Nimura, and S. Doki, “Position Sensorless Control of IPMSM in Overall Speed Range by Extended EMF,” 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE ’19 ECCE Europe), Genova, Sept. 2019.
[2] K. Kitamura, T. Nimura, and S. Doki, “Position Sensorless Control Method by Using Redefined Extended Electromotive Force for All-Speed-Range Drive of IPMSM and its Evaluation on Electric Vehicle,” 2020 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Delft, Netherlands, 2020