研究テーマ / Research topic
ロバストな自己位置推定を目指した 複数センサ情報の選択的統合法
| English ver. | Japanese ver. |
Autonomous Mobile Robot
Expectations are rising for autonomous mobile robots that recognize the surrounding environment and move autonomously with the on-board sensors.
In addition to robots for transportation, security, and cleaning, construction fields, social infrastructure/plant maintenance fields, and agricultural fields, we have an extremely wide range of application fields such as self-driving cars.
In recent years, autonomous mobile robots that are expected to be put into practical use are autonomous mobiles that can play an active role in people’s living spaces and disaster sites, where the environment is not prepared for autonomous driving.
In human living spaces and disaster sites, various environmental factors such as temperature, weather, seasons, and movements of people, and things change unpredictably.
In order to develop autonomous mobile robots that work safely in such an environment, it is necessary to improve the robustness of localization against environmental changes.
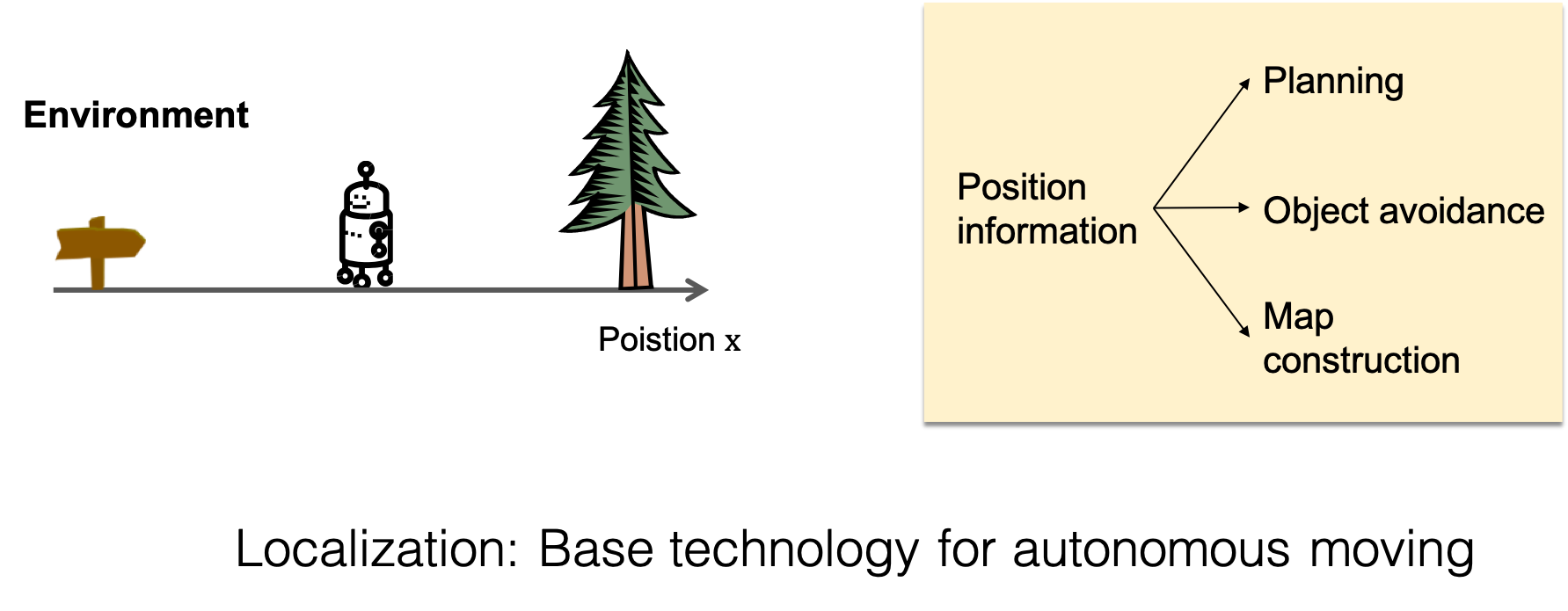
Localization is a technology that estimates its own position based on the observations of sensors mounted on the robot.
The estimated position is used for map construction, route generation, and obstacle avoidance in autonomous movement.
Most of the technologies of autonomous movement are designed based on the estimated position, and stable position estimation technology is important.
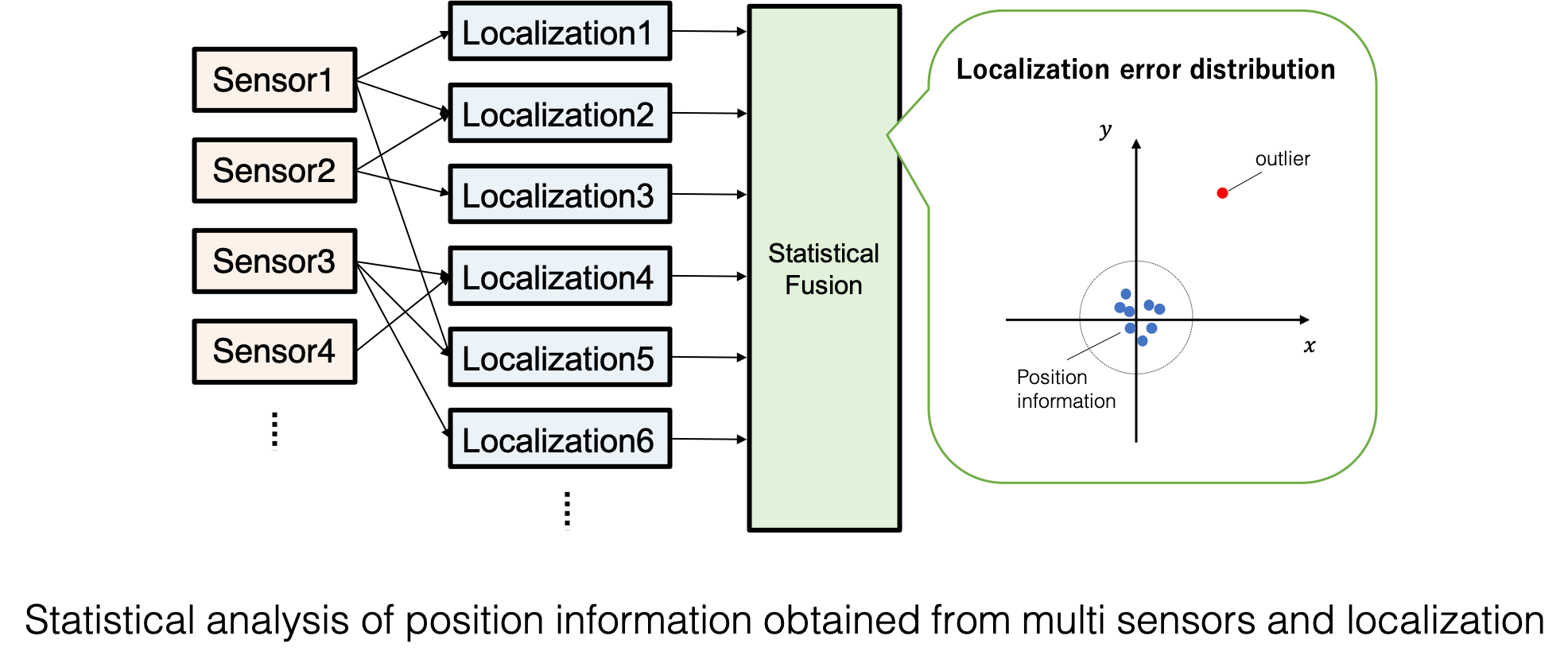
In this research, we aim to improve the robustness of localization by mounting a wide variety of sensors and localization methods and “statistically processing” the position information obtained from them.
Since each localization method processes sensor observations in different ways, it is assumed that the localization results would be different from each other.
Therefore, we assume that “position information including the same catastrophic estimation error is not calculated at the same time”.
Based on the above premise, we are studying a robust localization method for outliers with extremely large errors by comparing the position information obtained from each localization method with each other.
9E
自律移動ロボット

搭載されたセンサにより周辺環境を認識し自律的に移動する自律移動体への期待が高まっています.
搬送,警備,清掃などを行うロボット,建設分野,社会インフラ・プラント保全分野,農業分野に加え,自動運転車など,極めて広い応用分野を持っています.
近年,実用化が期待されている自律移動体は,自律走行用に環境が整備されていない,人の生活空間や災害現場で活躍できる自律移動体です.
人の生活空間や災害現場は,温度,天候,季節,人や物の動きなど多種多様な環境の要因が,予測不能に変化します.
このような環境下で安全・確実に動作する自律移動体を開発するには,環境変化に対する位置推定のロバスト性向上が求めれらます.
位置推定
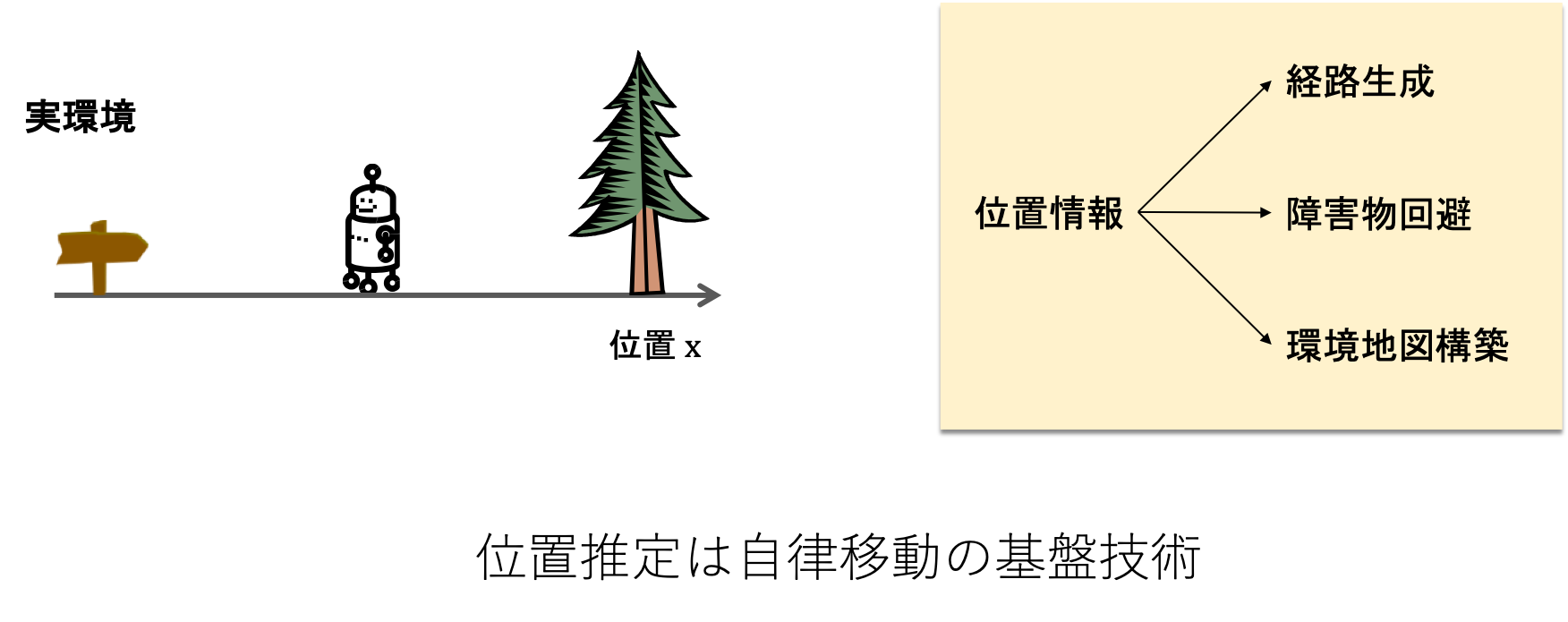
位置推定は,移動体に搭載されたセンサの観測を基に自身の位置を推定する技術です.
推定した位置は,自律移動における地図構築や経路生成,障害物回避において利用されます.
例えば,環境地図構築 – 推定位置を起点に環境に関するセンサの観測をマッピングし,移動体が走行する環境の地図を構築する技術 – では,移動体が推定した位置の精度が構築される地図の精度に非常に大きく関わります.
推定位置をもとに目的位置までの経路を生成する経路計画や自身に接近する可能性がある障害物を避ける障害物回避においても推定した位置が利用されます.
このように自律移動に必要な技術のほとんどは,推定された位置を起点として設計されており,安定した位置の推定技術が重要となります.
研究目的
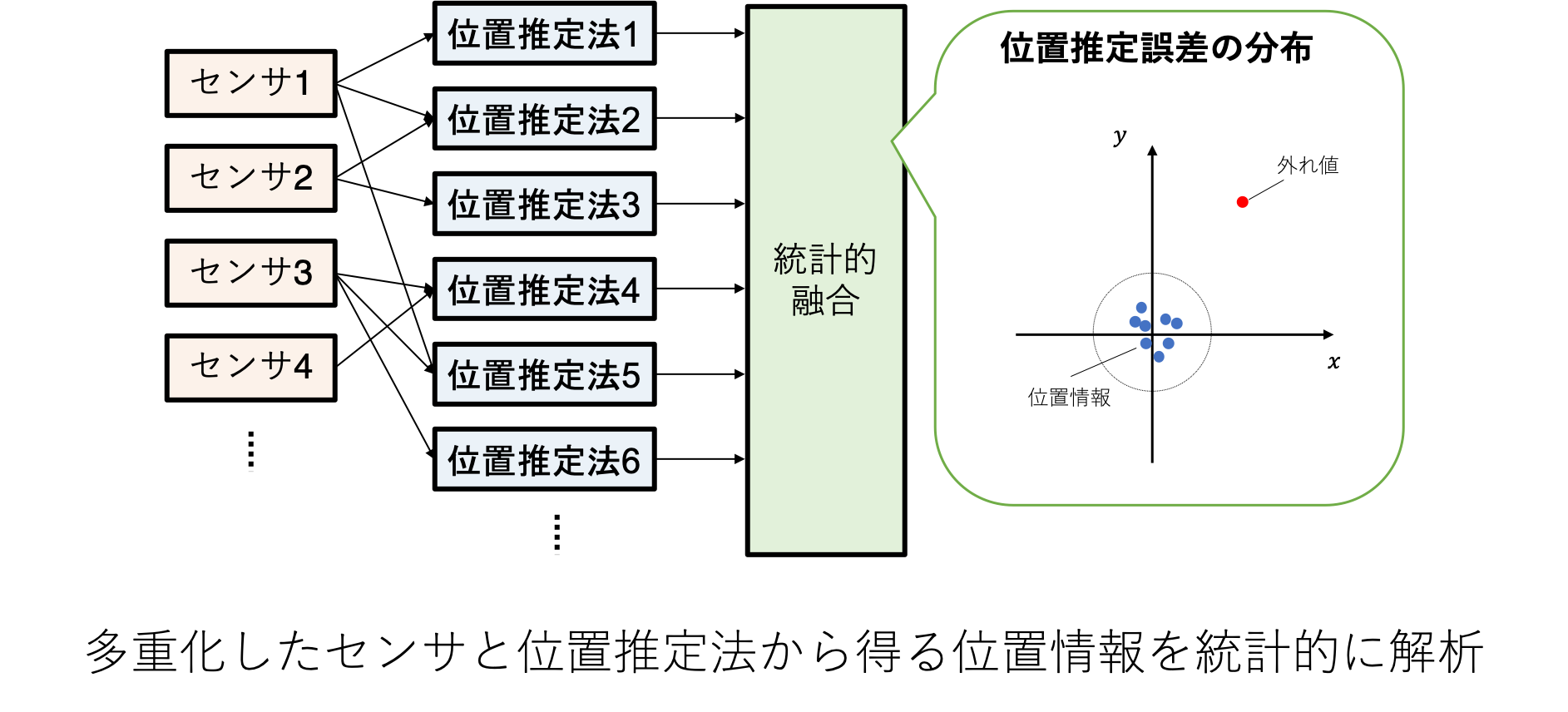
本研究では,移動体に多種多様なセンサ・位置推定法を搭載し,それらから得る位置情報を「統計的に処理」することで,位置推定のロバスト性向上を目指しています.
各位置推定法は,それぞれ異なる方法によりセンサの観測を処理していることから,位置推定結果は互いに異なることが想定されます.
そこで,「同時に同様の壊滅的な推定誤差を含む位置情報は算出されない」という前提をおきます.
その前提のもと,各位置推定法から得る位置情報を互いに比較することで,著しく大きな誤差を持った外れ値に対してロバストな位置推定法を研究しています.
研究の詳細は,以下のスライドをご確認ください.
これは、Office の機能を利用した、Microsoft Office の埋め込み型のプレゼンテーションです。