研究テーマ / Research topic
布状アクチュエータの用いたアシストスーツの実現/Realization of Assistive Suits with Fabric Actuators
| Japanese ver. | English ver. |
研究背景と目的
ソフトアクチュエータとは
ソフトアクチュエータとは軽量、柔軟な素材が変形することにより機能するアクチュエータです。例として下のような「McKibben型人工筋」が挙げられます。これは空気圧を加えることで収縮するという性質を持つソフトアクチュエータです。

空気圧式ゴム人工筋肉を使った歩行トレーニング装置[1]
左の画像はブリヂストン社の空気圧式ゴム人工筋肉を利用した歩行トレーニング装置です。組み込まれているソフトアクチュエータによって脚の曲げ伸ばしをアシストします。
布状アクチュエータの開発

先行研究にて開発された布状アクチュエータ
平ゴムを編んで作られた布の両面に,空気圧によって収縮するMcKibben型人工筋を配置することで,左図のような新しいソフトアクチュエータが開発されました[2]。既存のソフトアクチュエータの多くは収縮のみ、曲げのみといった1自由度の変形ですが、下の動画のようにこの布状アクチュエータは前屈、側屈、回旋といった自由度の高い変形が可能です。
また筒状に成形することもでき、単一のデバイスで幅広い3次元的動作が可能です。これを利用することで単一動作だけでなく自由度の高い動作もアシストできるアシストスーツの実現が見込まれています。
しかし先行研究では布状アクチュエータのアシストスーツへの利用可能性は未検討となっています。そこで本研究の目的は「布状アクチュエータを用いたアシストスーツの実現」です。
研究内容
目的達成の課題
布状アクチュエータをアシストスーツへ利用する際に、上図のような先行研究の布状アクチュエータだけでは問題点があります。それはこの人工筋の配置パターンおよび布地では身体の動きすべてを実現できないという点です。布状アクチュエータの可動域を変化させるためには人工筋の配置パターンおよび布地を変更しなければいけません。
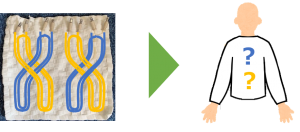
よって、アシストスーツ実現に向け、各身体部位に適した変形を実現できるように人工筋の配置パターンおよび布地を再検討する必要があります。
目的達成までのステップ
上記の課題を踏まえて、本研究は次のようなステップで進めています。

STEP1 布状アクチュエータ設計の自由度向上<完了>
既存の布状アクチュエータでは人工筋は布地の平ゴムに通して固定されています。しかし、このままでは人工筋の固定点位置が布地に依存し配置パターンが制限されてしまう、人工筋を通せる布しか動かすことができないといった制限があります。これらの制限を解消し、より多様な人工筋配置パターンや布地をアシストスーツに利用可能とするのがこのSTEP1の目的です。
STEP2 所望の変形を実現する布状アクチュエータの設計<検討中>

STEP1でより多様な人工筋配置パターンおよび布地が選択可能となった上で、スモールサイズで身体部位の動きを実現できる人工筋配置パターンおよび布地を模索していきます。
STEP3 アシストスーツの作成<検討中>
 STEP2で模索した人工筋配置や布地の知見をもとに、大人サイズのアシストスーツを作成し、所望の動きを実現できるか検討します。
STEP2で模索した人工筋配置や布地の知見をもとに、大人サイズのアシストスーツを作成し、所望の動きを実現できるか検討します。
English ver—————————-
Research Background
Soft Actuator
Soft actuators are actuators that function by deforming a lightweight, flexible material. For example, the “McKibben artificial muscle” as shown below. This is a soft actuator that has the property of contracting when air pressure is applied.

Gait training device using pneumatic rubber artificial muscles[1]
The image on the left shows Bridgestone’s gait training device using pneumatic rubber artificial muscles. The soft actuator used in the device expands and contracts by adding and subtracting pressure from the air in the rubber tube, assisting the bending and stretching of the legs.
Fabric Actuator

A new soft actuator, “fabric actuator” has been developed by placing pneumatically contracting McKibben artificial muscles on both sides of a fabric made of woven flat rubber, as shown in the left figure[2]. Most of the existing soft actuators have only one degree of freedom(DOF) of deformation, such as contraction or bending, but this fabric actuator can perform a high DOF of deformation, such as forward bending, side bending, and rotation as shown in the video below. It can also be molded into a cylindrical shape, allowing a wide range of three-dimensional movements with a single device.
This is expected to lead to the realization of assistive suits that can assist not only in single movements but also in highly flexible movements.
However, in previous studies, the possibility of using fabric actuators for assistive suits has not yet been investigated.
Therefore, the purpose of this research is to “realize an assistive suit using fabric actuator.“
Research content
Problem of Creating an Assist Suit
When using fabric actuators for assistive suits, there is a problem with the fabric actuators in the previous study alone, as shown in the figure above. In order to change the range of motion of the fabric actuator, it is necessary to change the pattern of the artificial muscles and the fabric. In order to change the range of motion of the fabric actuator, we need to change the artificial muscle placement patterns and fabric.

Therefore, it is necessary to examine the artificial muscle placement and fabric to achieve the appropriate deformation for each body part.
3 Steps to Achieve Goal
Based on the above issues, this research is proceeding in the following steps.

STEP1 Improve DOF of Fabric Actuator Design :Completed
In the existing fabric actuator, the artificial muscles are fixed through the flat rubber of the fabric. However, as it is, there are limitations such as the fixed position of the artificial muscle depends on the fabric and the placement patterns are limited, and only the fabric that can pass the artificial muscle can be moved. The purpose of this STEP 1 is to eliminate these limitations and make a wider variety of artificial muscle placement patterns and fabrics available for assistive suits.
STEP2 Design Fabric Actuator to Achieve Desired Deformations :Working
 After the selection of various artificial muscle placement patterns and fabrics in STEP 1, we will search for artificial muscle placement patterns and fabrics that can realize the movement of body parts in small sizes.
After the selection of various artificial muscle placement patterns and fabrics in STEP 1, we will search for artificial muscle placement patterns and fabrics that can realize the movement of body parts in small sizes.
STEP3 Create Assist Suits :Working
 We will create an adult-sized assistive suit based on our knowledge of artificial muscle placement and fabrics explored in STEP 2 and consider whether the desired movement can be achieved.
We will create an adult-sized assistive suit based on our knowledge of artificial muscle placement and fabrics explored in STEP 2 and consider whether the desired movement can be achieved.
[1]Rentec Jornal「Vol.141 空気圧式ゴム人工筋肉を使った歩行トレーニング装置」journal.orixrentec.jp/2018/02/post-57.html
[2]Y. Funabora. Flexible fabric actuator realizing 3d movements like human body surface for wearable devices. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 6992–6997, 2018.