研究テーマ / Research topic
身体との接触状態に着目した体幹部全体の支援を行う装着型ロボットの開発
目次
|
|
装着型アシストロボットとは?
What is Wearable Assist Robot?
|
装着型アシストロボットは,人体に直接装着して装着者の動作支援を行うロボットです.とりわけ,運搬・介護現場における労働者の身体的負担軽減用途への適用が期待され,CYBERDYNE社をはじめとする様々な機関で研究開発が行われています.現状,腰部・腕部・脚部を支援するロボットは既に実用段階にあり,実現場への導入事例も報告されています(Fig.1).
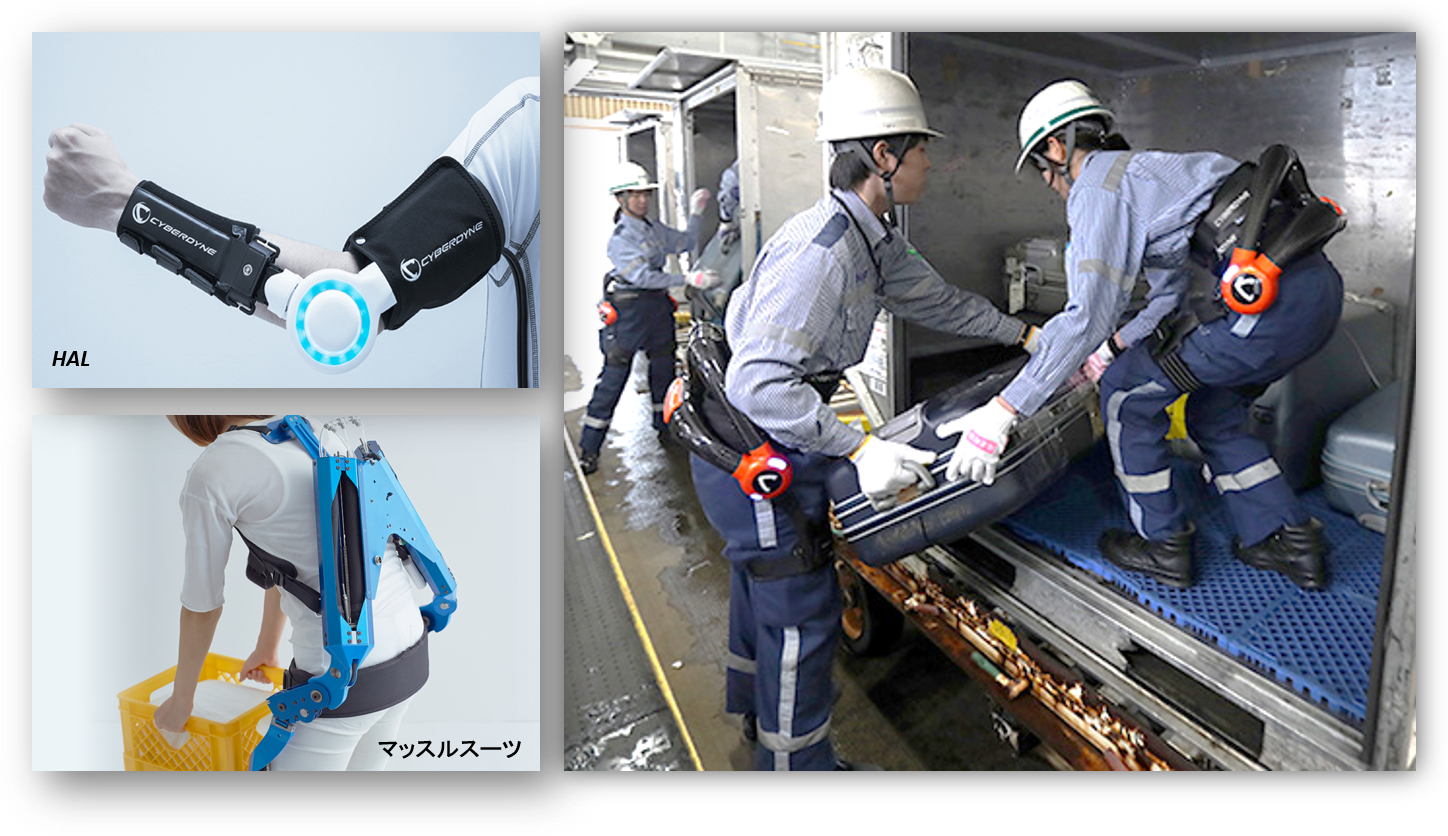

Fig.1 Wearable assist robots in practical use (CYBERDYNE, INNOPHYS, ANA)
一方で,介護従事者の身体的負担は,腰部のみならず首から腰にかけての体幹部全体に渡ることが,大阪府立公衆衛生研究所の調査で明らかになっています(Fig.2).そこで,本研究では未だ研究段階である,体幹部全体を支援可能なロボット『体幹部装着型ロボット』を実現し,更なる介護従事者の負担軽減を目指します.
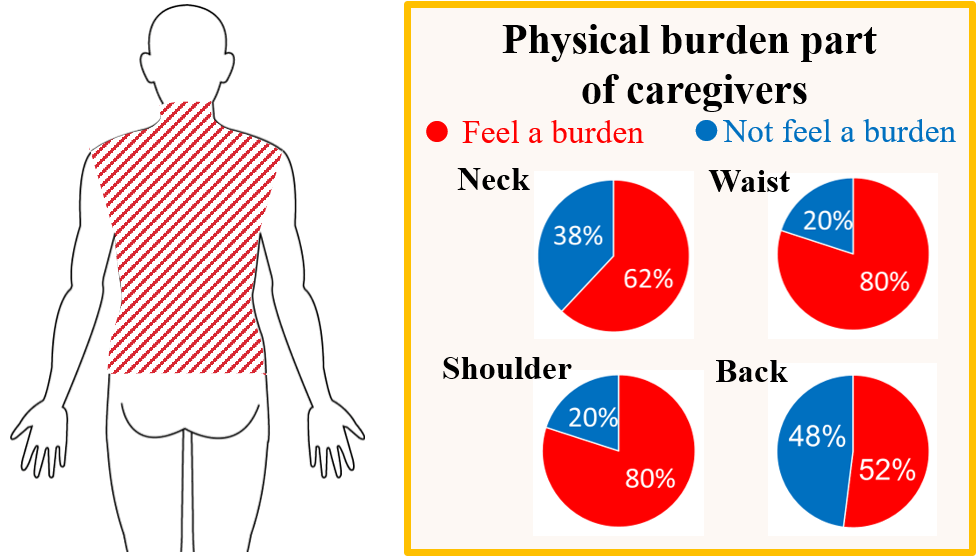
Fig.2 Body parts where caregivers feel physical burden
What is Wearable Assist Robot? (Eng.)
The wearable assist robot is a robot that wears directly on the human body to support human motion. In particular, it is expected to be applied for reducing the physical burden of workers at transportation and nursing care sites, and has been researched at various organizations including CYBERDYNE. At present, robots that support the lumbar, arms, and legs are already in the practical stage, and examples of introduction to realization sites have been reported.
On the other hand, it has become clear from a survey by the Osaka Prefectural Public Health Research Institute that the physical burden of care workers extends to not only the waist but also the entire torso (Fig. 2). Therefore, in this research, we aim to realize a robot that can support the entire torso, which is still at the research stage, and try to reduce the burden on the care workers further more.
|
|
体幹部装着型ロボットの課題
Problem in Realization of Wearable Assist Robot for Entire Torso
|
本章では,既存のロボットとの比較を交えながら体幹部装着型ロボットの課題について述べます.一般に,装着型ロボットには① 構造決定,② 制御法の二つの設計要素があります.下図と合わせて,それぞれの観点から課題を説明します.
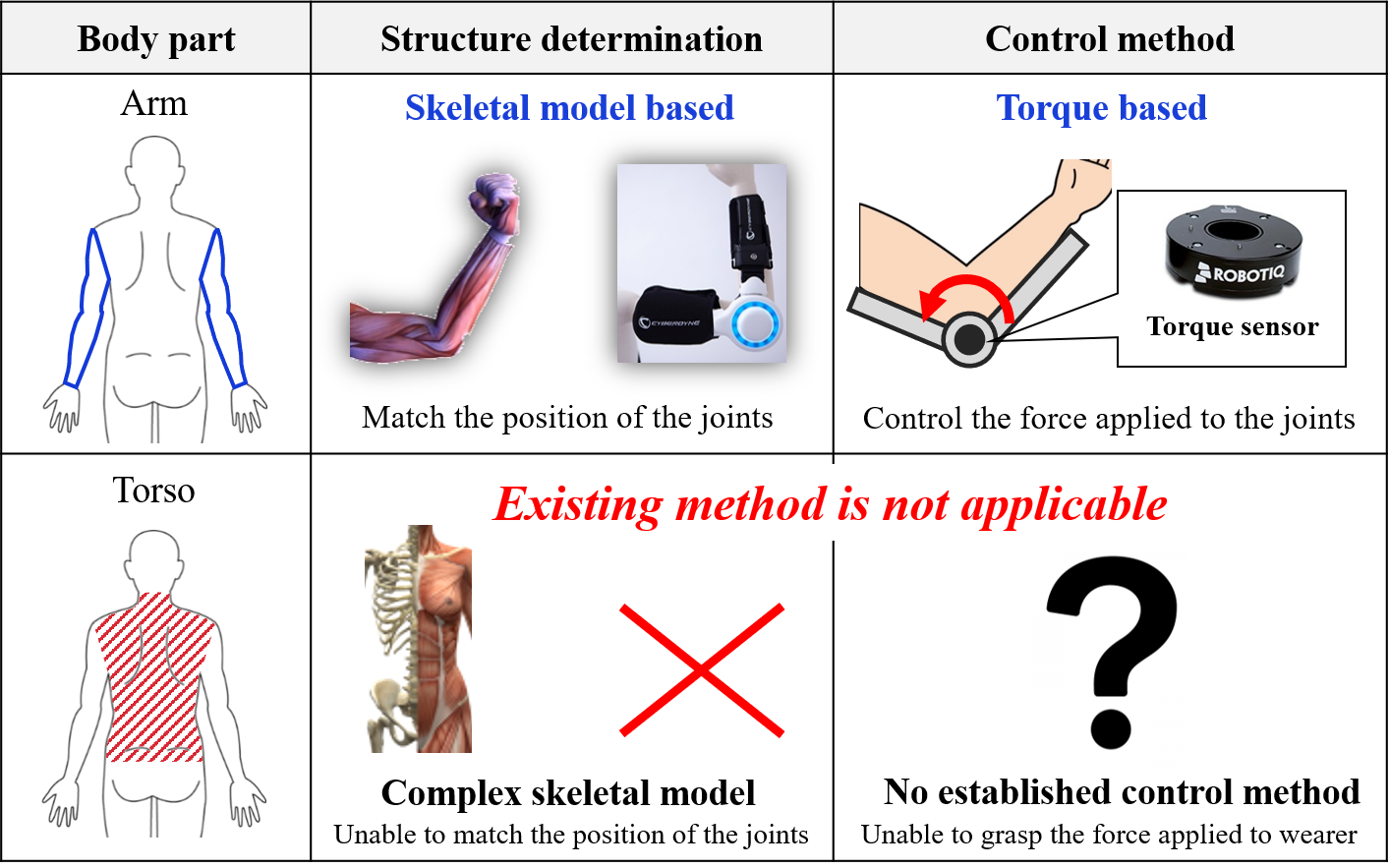
Fig.3 Comparison with existing robots
① 構造決定について
既存のロボットは,人の筋骨格モデルに基づきロボットと身体の関節配置が一致するように構造が決定されました.これによって,ロボットが人の動作に追従することが可能となります.一方で,体幹部は20以上の関節で構成される多関節部位であるため,既存のロボット同様に関節配置を一致させることは非現実的です.すなわち,体幹部装着型ロボットの構造決定においては,筋骨格モデルを適用することができず,どのような構造であれば動作支援が可能であるかを検証しなければなりません.
② 制御法について
既存のロボットは,関節部に取り付けたトルクセンサを用いて,身体の関節部に加わる負荷を把握することで安全な動作支援を実現しました.先にも触れたように,体幹部装着型ロボットでは人の関節数・配置と一致させることが困難であるため,この制御法では人に加わる負荷を把握する事ができず,装着時の安全性を担保することができません.すなわち,体幹部装着型ロボットの制御法構築においては,装着時の安全性を如何に確保するかを念頭に置いて設計しなければなりません.
以上のように,体幹部装着型ロボットの実現のためには,従来とは異なる観点から,構造決定・制御法における課題を解決する必要があります.
Problem in Realization of Wearable Assist Robot for Entire Torso (Eng.)
In this chapter, we will describe the problems of the body-mounted robot while comparing it with existing robots.
① Determination of Robot Structure
The structure of the existing robot has been determined based on the human skeletal model so that the joint arrangement between the robot and the body matches. This makes it possible for the robot to follow human movements. On the other hand, it is unrealistic to match the joint arrangement as well as existing robots because the trunk is an articulated part consisting of more than 20 joints. In other words, skeletal models can not be applied in determining the structure of a body-worn robot, and it is necessary to verify which structure can support motion.
② Control method
The existing robot realized safe operation support by grasping the load applied to the joint part of the body using the torque sensor attached to the joint part. As mentioned above, it is difficult to match the number and arrangement of human joints in a wearable robot for torso. Hence, the existing control method can not grasp the load applied to the human body, and the safety of wearing can not be secured. In other words, in constructing a control method for a wearable robot for torso, it is necessary to design with consideration on how to secure safety of wearing.
|
|
『接触』に着目した体幹部装着型ロボット
Wearable Assist Robot for Entire Torso Focused on Contact with wearer
|
本章では,当研究室が提案する体幹部装着型ロボットのコンセプトについて述べます.本研究では,体幹部装着型ロボットの構造決定・制御法構築にあたり,身体との『接触』に着目しています.
Fig.4に示すように,ロボットの力は身体との『接触』により装着者へと伝達されます.そのため,装着者に加わる『接触力』を直接計測することができれば,装着者への局所的な力の集中等の危険な状態を見逃すことなく,装着時の安全性を確保することができるはずです.センサ技術の進展を背景に,圧力分布センサと呼ばれる力分布情報を計測可能なセンサが近年市場に出回り始めました.本研究では,この圧力分布センサをロボットと身体の間に搭載することで,人に加わる力を『接触力分布』として把握します.その上で,意図した『接触力分布』に制御することが可能な装着型ロボットを実現し,安全な体幹部支援を達成します.
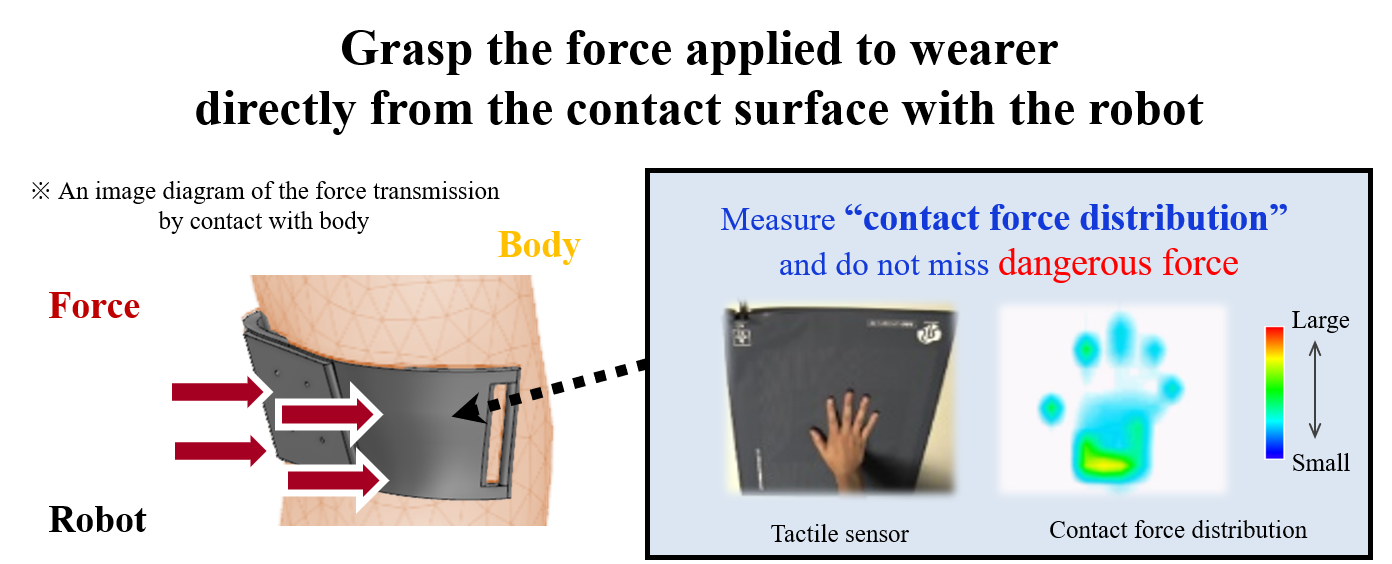
Fig.4 Concept of our robot
Wearable Assist Robot for Entire Torso Focused on Contact with Wearer (Eng.)
In this chapter, the concept of the proposed robot is described. In this research, we focus on “contact” with the body in order to construct the structure determination and control method of the robot.
As shown in Fig. 4, the force of the robot is transmitted to the wearer by “contact” with the body. Therefore, if “contact force” applied to the wearer can be measured directly, safety at the time of wearing should be secured without missing dangerous conditions such as concentration of local force on the wearer. With the development of sensor technology, sensors that can measure force distribution information, called tactile sensors, have recently been on the market. In this research, by mounting this sensor between the robot and the body, the force applied to a person is grasped as “contact force distribution”. Based on that, we realize a wearable robot that can be controlled to the intended “contact force distribution” and achieve safe body support.
|
|
『体表面形状計測・解析』に基づく構造決定
Structure Determination Method Based on Body Surface Shape Measurement and Analysis
|
本章では,体幹部装着型ロボットの構造決定について説明します.提案するロボットを実現するにあたって,満たすべき構造上の条件は以下の2点です.
・人の動作に追従することが可能である
・接触力分布を漏れなく適切に計測可能である
以上の条件により,次の制約が生じます.適切に接触力分布を計測するためには,接触力が正確に伝達される堅い素材でロボットを構成する必要があります.また,漏れなく接触力分布を計測するためには,動作によらずロボットが常に身体にフィットしている必要があります.
これらの条件・制約を考慮したうえで,実際にロボットが接触する『体表面形状』に着目した構造決定法を構築しました.この手法は,【人の動作に伴う体表面形状の変形を計測・解析し,変形の小さい体表面領域にその体表面形状に即したリンクを配置することができれば,身体とロボットのズレを最小限に抑制可能である】という考えに基づいています.構造決定法の概要については,以下の動画をご覧ください.
Structure Determination Method Based on Body Surface Shape Measurement and Analysis (Eng.)
In this chapter, we will explain the structure determination of a body-worn robot. In order to realize the proposed robot, the following two structural conditions should be satisfied.
・ It is possible to follow human movement
・ Can measure contact force distribution properly without leakage
Under the above conditions, the following constraints arise. In order to measure the contact force distribution properly, it is necessary to configure the robot with a hard material to which the contact force is accurately transmitted. Also, in order to measure the contact force distribution without leakage, the robot must always fit to the body regardless of the movement. Taking these conditions and constraints into consideration, we constructed a structure determination method that focused on the “body surface shape” that the robot actually contacts. If this method can measure and analyze the deformation of body surface shape caused by human movement and arrange the link according to the body surface shape in the small deformation body surface area, the displacement between the body and the robot is minimized As long as it can be For an overview of the structure determination method, please see this video.
|
|
『接触力分布』をフィードバックする制御法
Control Method Which Feeds Back Contact Force Distribution
|
本章では,体幹部装着型ロボットの制御法について説明します.提案するロボットでは,人に加わる力を意図した『接触力分布』に制御することで安全な体幹部支援を実現します.
Fig.5は,我々が構築した『接触力分布』をフィードバックするロボット制御系のブロック線図を表しています.コントローラには,ロボットに搭載した圧力分布センサが取得した『接触力分布』,および,『接触力指令分布』が入力として与えられます.そして,コントローラ内部で,接触力指令分布に最も近づくロボット姿勢を順運動学に基づき算出し,ロボットに関節角指令を印加します.これによって,意図した『接触力分布』を達成するロボットの姿勢制御を実現します.
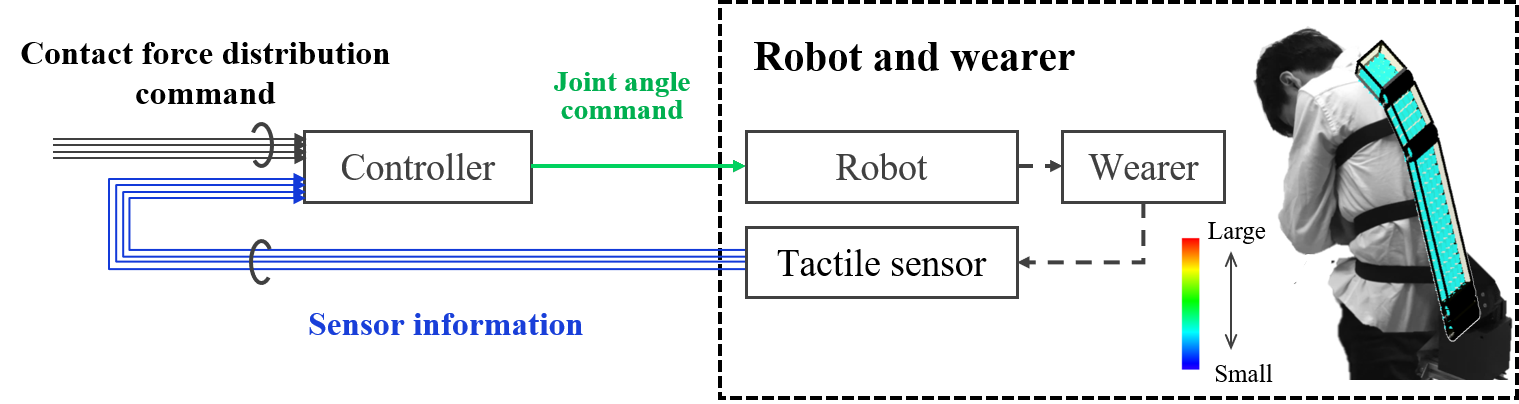
Fig.5 Control system that feeds back contact force distribution
Control Method Which Feeds Back Contact Force Distribution (Eng.)
This chapter describes how to control a body-mounted robot. In the proposed robot, safe body support is realized by controlling the contact force distribution intended for human beings.
Fig. 5 shows a block diagram of a robot control system that feeds back the “contact force distribution” we built. The controller receives the “contact force distribution” acquired by the pressure distribution sensor mounted on the robot and the “contact force command distribution” as input. Then, within the controller, the robot posture closest to the contact force command distribution is calculated based on forward kinematics, and the joint angle command is applied to the robot. This achieves robot attitude control that achieves the intended “contact force distribution”.
|
|
現在の取り組み『実機制作』
Current Initiatives
|
現在は,提案するロボットの動作支援効果・安全性を検証するために,実機の制作を行っています.持ち上げ動作の支援を想定して,前屈動作に伴う体表面形状の変形を計測・解析した結果,3リンクのロボットであれば動作に対応可能であることが明らかになりました(Fig.6参照).そして,3DCADソフトを駆使して設計を行い,3Dプリンタを用いて制作を進めています.

Fig.6 Design of wearable robot for entire torso
目下制作中のロボットの構成をFig.7に示します.各リンクの形状は,接触する体表面形状に即した形状になっています.サーボモータをリンク間に搭載し,リンク間に相対回転を付与することで持ち上げ動作に追従します.リンク内側に直接圧力分布センサを貼付することで,人の体表面に加わる力を『接触力分布』として計測します.実際に制作したロボットを被検者に装着してもらい,動作に応じた『接触力分布』を計測可能であることを確認しました(Fig.8参照).今後は,制御法の実装に着手し,被験者実験を通じて提案するロボットの動作支援効果・安全性を定量的に検証していきます.
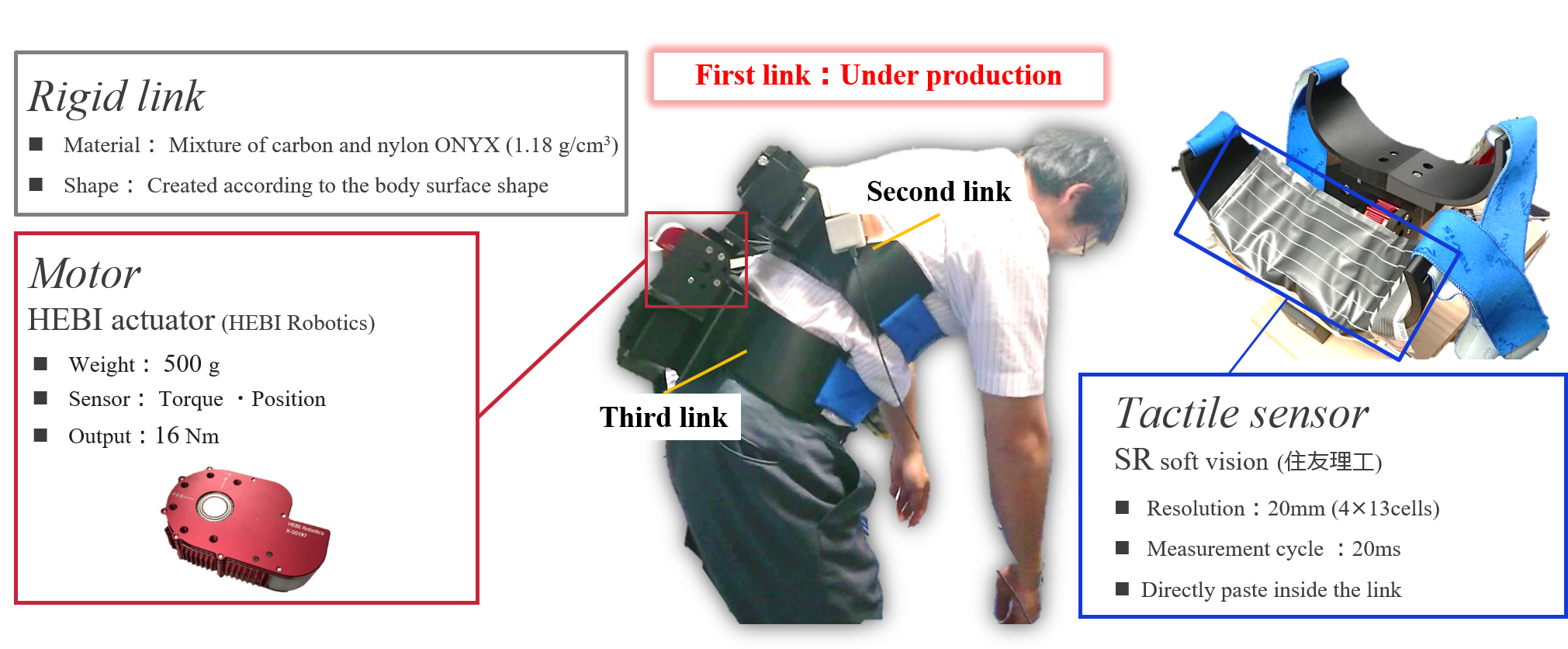
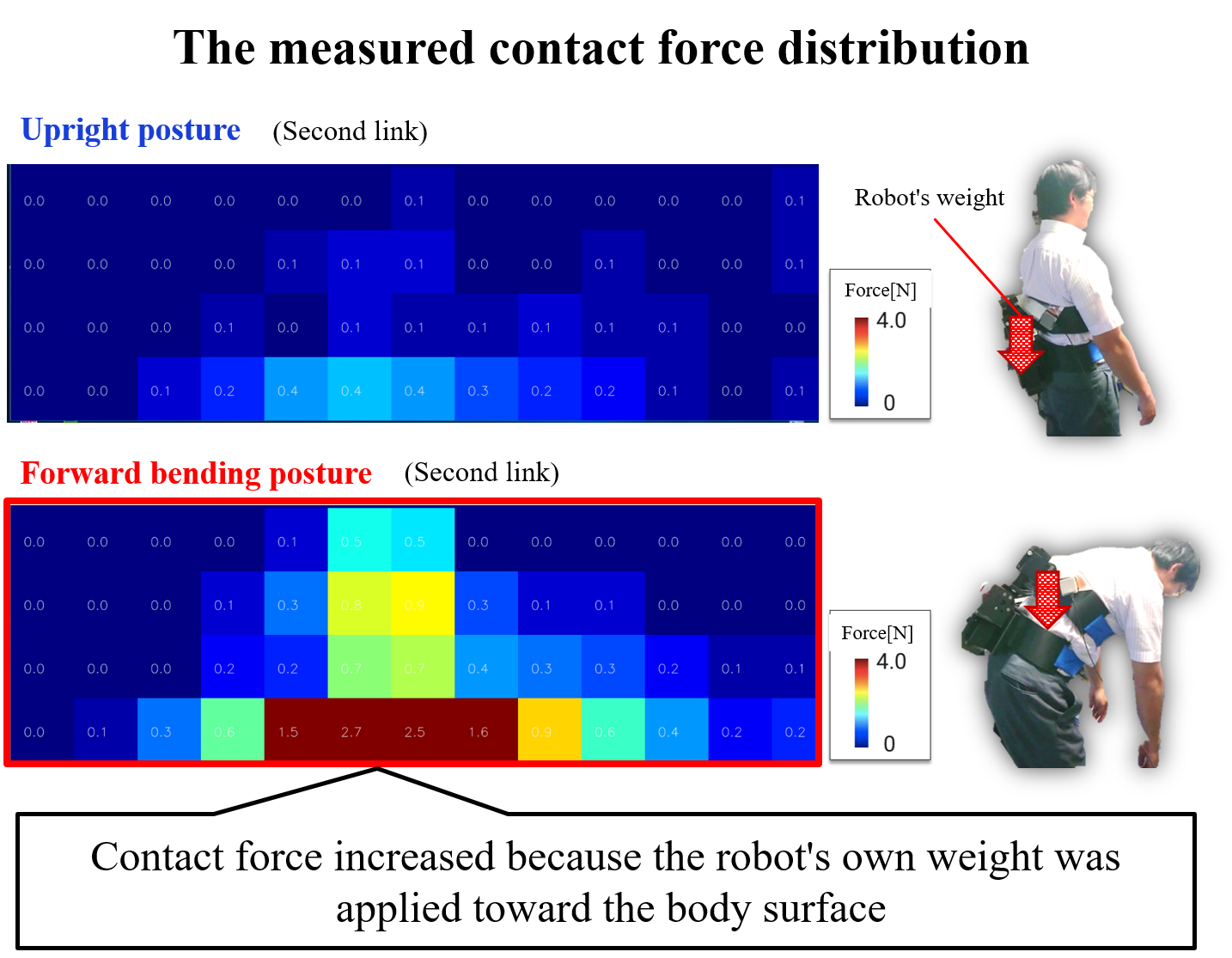
Fig.7 Contact force distribution that changes according to the posture
Current Initiatives (Eng.)
Now, we are producing a real machine to verify the operation support effect and safety of the proposed robot. As a result of measuring and analyzing the deformation of the body surface shape accompanying the forward bending motion assuming support of the lifting motion, it became clear that the 3-link robot can cope with the motion (Fig. 6). And we design using the 3D CAD software and proceed with production using the 3D printer.
The configuration of the robot currently being produced is shown in Fig.7. The shape of each link conforms to the shape of the body surface in contact. A servomotor is mounted between the links, and relative movement is applied between the links to follow the lifting operation. By attaching a pressure distribution sensor directly inside the link, the force applied to the human body surface is measured as “contact force distribution”. We asked the subject to attach the robot actually produced, and confirmed that it was possible to measure the “contact force distribution” according to the movement (Fig. 8). In the future, we will start implementing the control method and quantitatively verify the effectiveness and safety of the proposed robot’s motion support through subject experiments.
【謝辞/Acknowledgement】
本研究はJSPS 科研費若手研究(A)16H05915 の助成を受けて実施したものです.
【出典一覧/Reference】
[1]Aviation Wire 『ANA、ロボットスーツ「HAL」検証継続 25台導入で分野拡大』
http://www.aviationwire.jp/archives/115551
[2]大阪府立公衆衛生研究所『高齢者介護サービス従事者の腰痛頸肩腕障害の軽減策に関する調査』
[3]CYBERDYNE株式会社『HAL®介護支援用(腰タイプ)による介護現場での労務環境の改善効果を発表 ~介護職員の負担を軽減,離職防止に効果〜』
[4]株式会社イノフィス『いきいき職場を目指す,埼玉医科大学グループ 光の家療育センターでは 職員の腰痛対策として,介護ロボット「マッスルスーツ(R)」を導入』
[5]永井 清 他 『エスコート型リハビリロボットの構造解析』
【関連研究/Related research】







